Neuromarketing techniques include a wide range of tools. to map, chart neuronal action, and understand how our brain responds to various somatosensory stimuli.
Definition.
Neuromarketing is a commercial marketing communication field that applies neuropsychology to market research, studying consumers' sensorimotor, cognitive, and affective response to marketing stimuli.
The potential benefits to marketers include more efficient and effective marketing campaigns and strategies, fewer product and campaign failures, and ultimately the manipulation of the real needs and wants of people to suit the needs and wants of marketing interests. Wikipedia
Neuromarketing Techniques applied to Conversion, CRO and SEO
The way we search on Google, how we choose the best response from the search engine, has a lot to do with that irrationality as well.
Therefore, web positioning has a lot to take advantage of the attitudes of users.
But where we can definitely perform better with these psychological elements is in our CRO (Conversion Rate Optimization) strategy.
As in the physical world, consumers repeat their biased attitudes in the process of buying and interacting on websites.
We act with the same irrationality both in the aisle of a supermarket and on a website where we go to buy.
Understanding how these cognitive biases work and how we react to certain stimuli will help you increase your conversions.
1. Anchoring
This effect refers to the tendency to get too carried away by the first impression and to condition our vision of the future according to that impression.
That is to say, our mind gives excessive importance to the first piece of information that we receive and later we value it according to that first information.
► Use powerful titles, images, and videos.
► Impact the user on your landing pages with powerful interactions or messages. (You are in good hands/Multiply your brand by 10)
► You can refer to questions that already exist in the mind of the user. (You want more leads, you want more users ...)
Note: When we just started out We used services like grammarly, hemingway editor, and supremedissertations which helped us get the perfect title and landing pages.
2. Authority Effect
► Do Influencer Marketing.
► Use prescribers in your sector.
► Show popularity, support for your brand.
► Give visibility to the prestigious awards that endorse your brand.
3. Availability cascade
The more an approach is reaffirmed and events that reinforce it occur, the more effectively it penetrates the mind of the user.
Keep these tips in mind:
► Work better on your content, copy, design and increase visibility.
► Create very viral campaigns that make you spend a long time on people's lips
A good example is Oreo's Daily Twist campaign, which got a lot of engagement.

4. Backfire effect
Sometimes a user receives rational information that denies his beliefs and even so, he asserts himself more in them.
Many times, these messages from outside, far from persuading us, reaffirm us about our starting ideas. It usually happens with political opinions.
One way to take advantage of this bias is to detect the bias that the user has and work from there.
It is not difficult to find landing pages that play with this resource. The main idea is to agree with the user, reinforce that prejudice to capture their attention and from there, try to convince them otherwise and thus improve the conversion.
5. The importance of the result
Users usually evaluate the quality or importance of something based on figures or results.
The results can be supported in words, but the numbers help improve the conversion much more.
► Include figures that guarantee that your service is good for our users.
Check out Andcards homepage to get the best ideas on how to use images to reinforcetrust .
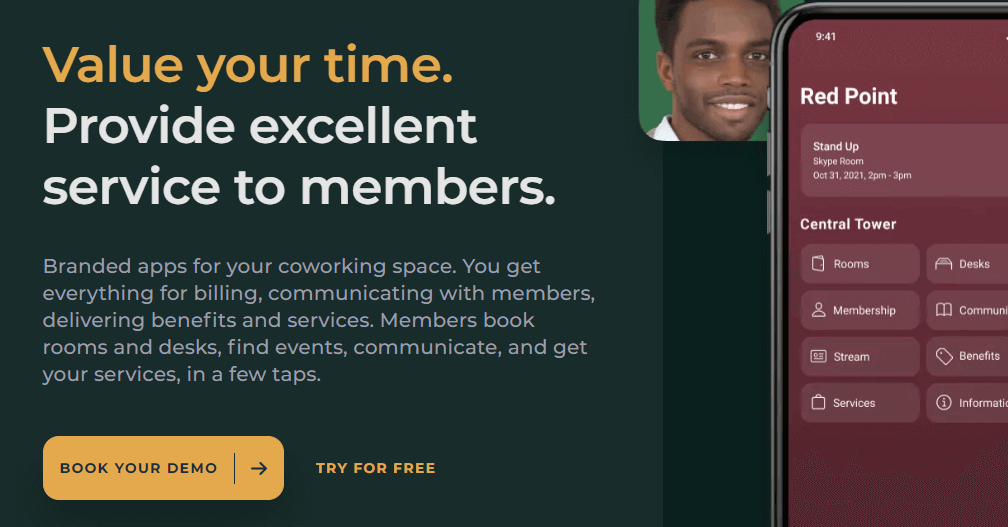
6. The trend effect
People are more willing to consume what others consume and to think what influencers think. For example:
► Detect which are the influencers in your sector and try to influence their communities.
► Add social proof in the form of numbers and testimonials in friction zones, conversion forms, sales, etc.
► Add testimonials, and support them in some way (link to social networks)
“In SEO, the rating stars show that several users have endorsed the quality of content. It help in generating trust and in closing more sales” - Nicole SEO hea
7. Credibility bias
One of the elements that make the consumer doubt the most is the price. Oftentimes, when it is too low, users distrust and stop buying.

If an argument sounds too good to be true, then we can see it as false, we distrust it.
When your prices are lower than the market, justify why if necessary.
You may not have a series of expenses that allows you a different price margin than the competition (not having a physical store, fewer intermediaries, etc).
If so and you see that it is beneficial for your business, let your users know it.
8. Comparison
Users constantly compare and draw their own conclusions.
► Take advantage of this bias to optimize your SERPs. We can take advantage of this behaviour, for example, when designing our meta descriptions.
Good titles, adding elements like rich snippets, rating stars and everything that makes our SERP stand out.
9. Mirror effect

This effect means that when we see someone doing something, we imagine ourselves doing it.
One of the most widespread elements of neuromarketing is mirror neurons. Due to its operation, when we see someone doing something, we unconsciously imagine ourselves in the same situation.
► Show your product or service in action. Show a person enjoying your services or products through photos or videos. Make the user visualize himself using that service or product.
► Go to storytelling; create a story where the protagonist looks a lot like the user or has the same needs. This way you will feel identified.
If you don't feel you have enough storytelling skills, delegate this task to expert copywriters of TrustMyPaper.
They will make your content engaging and help reach your goal - generate empathy of users.The important thing is to generate empathy in the user.
When selling, show your products/services being used by other people. You will improve your conversions
10. Need to solve problems
A large percentage of users buy something to solve a problem or whatever they identify as such.
This is precisely the root of marketing: brands are at the user's disposal to help solve problems. It is not about you, your product, but how you are going to help your customer meet a need.
► Remind your customers of thier problems, tell them you understand and show them how you can help.
11. Need to be part of a community
We tend to want to fit into a group, we like to be part of a community. Beyond a rational preference, it seems that we have the need to be part of a herd in our brains.
Many bloggers resort to this human reaction and use it in their pop-up copywriting to attract subscribers.
12. Contrast effect
The reduction in the perception of something when compared to another element that contrasts strongly.
The pricing plans of many websites successfully take advantage of this bias. They propose three alternative plans to the user and try to make one of them stand out from the rest.
The Color is an element that gives a lot of play in this regard in highlighting one of the plans. You can also help the size or texts as "Option most valued by users."
The conversion works much better when comparing between 3 options and not so much when we give the user a choice between A or B.

13. Reciprocity
We tend to reciprocate when we feel benefited. This is great news for content creators. Many times we want to viralize content, spread it, that it reaches more public.

The best way to achieve this is by creating quality content that helps the user, that adds value. Possibly, in reciprocity, that user voluntarily shares our content, recommends it through links or mentions.
However, it must be taken into account that if the user considers that the price to pay is too high, he will not pay it.
This bias applies a lot when it comes to getting customers online. When it comes to capturing leads in exchange for valuable content, let's make simple forms that do not involve an effort for the potential lead.
If you create quality content that adds value to the user and helps them, the user will reward your work
14. Halo effect
It consists of attributing a general characteristic to something from a single detail. That is, from a single element (often visual) we infer a lot of other characteristics.
We associate them automatically, in the same way, that we associate the beautiful with the good.
It has been widely used in advertising by placing trusted figures and famous people as the face of our products.
15. The offence of knowledge
Pretend to speak to your users as if they were you, at a technical or high level, without thinking that they are not like you or speak like you.
Again, it's not about you, but about your customer or audience.
If your user does not speak your technical language, create closer and more understandable content.
Take this into account when designing your visual communication strategy, your copy and your design.
16. Empathy
Users react very well when treated with empathy. Brands must do an exercise in putting themselves in the shoes of consumers.
The more empathy, the easier it will be to connect.
It is important to convey that connection and empathy in our images, videos, texts and even in small elements like a subscribe button. It will help you reach your target audience with the right message and tone of voice.
17. Iconic sensory memory
It is an immediate memory based on visual stimuli. It is a component of the visual memory system, which also includes visual short-term memory and long-term memory.
Let's make landing pages so visually impressive that they remain in the user's memory.
18. Effect of Primacy
We pay close attention to the first information received about something. That is, when faced with a list or of elements, we tend to remember the first and last element.

The Brain Forgets The Middle
This applies to a product catalogue or the text of a web page. Let's bet on landing pages that as soon as they enter they surprise the user, they impact them.
It works for prices too. Websites like Booking usually launch a first price that it tends to lower.
However, the user keeps that first price as “the real price”. The next thing will be all sales and discounts that improve the conversion.
19. The tendency to immediate satisfaction
The brain tends to seek the reward as soon as possible and in the simplest way possible.
► On your websites, reduce the time and distance to the reward. As we see in this example ( from Uber ) , as soon as we land they are offering us a reward.
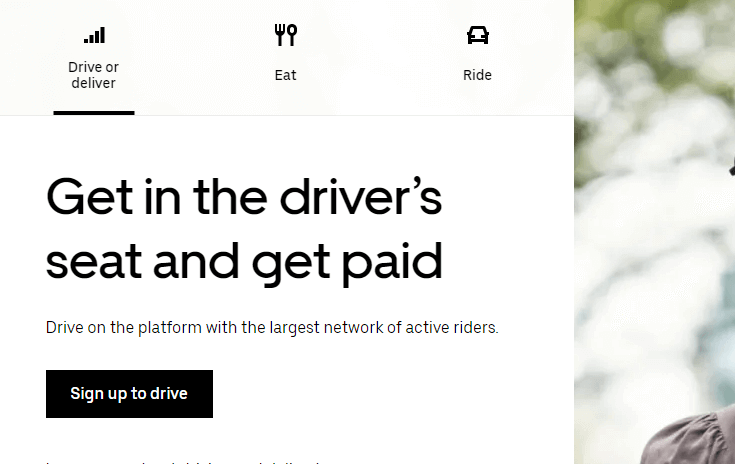
20. The tendency to reduce uncertainty
The brain tends to want the security or certainty of something as soon as possible. Help your clients to solve as soon as possible what causes them concern.
With regard to content creation and web positioning, we can work our SERPS taking advantage of this bias.
For example, you can ask a question in the title and show the solution to that question in the article's own meta description.
If the user sees that within the article is the solution to what he has to solve, he will click on your post.
21. The illusion of control/choice
The brain sends signals of well-being when you feel that you are in control or free to do whatever you want. Make your user feel that he is in control of the situation, that he is free to choose.
Throw questions to your user from your website in a tone that makes him the protagonist:
► What do you want to improve in your service?
► When do you want to achieve your next sales goal?
► In what time do you want to reach 20,000 subscribers on your YouTube channel?
22. Frame effect
Depending on how the information is presented, different conclusions can be drawn.
Within the web, there are many aspects that we can optimize according to this "framework". Try to give the most positive version of the information.
How you present your value proposition is just as important as the actual value of your proposition. For example :
► It is better "75% of users get it" versus "Only 25% of users don't get it"
► If you are going to present prices, it is better to do it on a monthly basis and not annually. Make sure the figure looks its best. 199 is better than 200.
► If you are going to present long forms, do it step by step, so that the user's first impression is not negative.
23. Need to touch the product
There are more possibilities of sale if the user can touch the product and feel that it is in their hands. That works mostly for eCommerce.
To bring the buyer as close to the product as possible, make it as tangible as possible. Product websites like Canon, Sony or Nike are good examples of how to do it right. When creating this type of content:
► Create large images
► 360 turns
► Image mapping
► Include videos or audios if your product profile demands it.

24. Post-purchase rationalization
It is about the tendency to justify the purchase after having made it through rational arguments. Paying hurts us. When we pay, the pain zone of the brain is activated.
► Help your user to reduce that pain.
► Place reviews Rich ( Rich Snippets )
► Reinforces the advantages of the product you bought
► Send a post-purchase transactional email with more information
25. Attention (Mere exposure)
We pay more attention to our recurring thoughts, to our ideas, reinforced over time.
Think about your brand in the long term, with a global vision, do not stick to isolated and disconnected campaigns.
Try that your brand is always present in a positive way in the minds of consumers. Run retargeting campaigns, create events ... etc.

26. Confidence / Familiarity effect
A user doesn't convert if they don't trust the brand.
Incorporate security elements on the web, show them that it is a safe site, give them guarantees to finish the conversion.
► You can incorporate security certificates, any kind of logo or banner that stimulates confidence at the time of purchase and eliminates any insecurity or fear in the user.
27. Postponement of purchase
There is a difficulty in consummating the act of purchase due to the expense of important decision-making involved.
Many times people enter eCommerce, select items and leave them in the cart.
They may consciously consider that they are not going to buy that product, however, they have already taken a step, they have already declared their intentions.
► Enable a " buy later "option on your eCommerce website, so that you have that cart on hand at a later time when you are ready to close the purchase.
28. The Last Unit Bias.
This bias refers to the tendency we have to want to consume the last parts or units of a whole.
This may be one of the most common and easy-to-find biases. It is very helpful on booking pages such as Booking.com and numerous online stores.
A " last 3 units " notice in red can be very persuasive and make the customer decide to close that online purchase for fear of running out of it.
29. Urgency effect
Hand in hand with the previous one goes the urgency effect, which is the tendency to want to consume something if there is little time left to do so because " the supply is running out ."
That is, if, in the previous bias, the determining factor was the last unit, here it is time.
In addition to the colour - usually red - or the typography, you can combine other elements that reinforce the sense of urgency. This is the case with counters, countdowns, etc.
30. Impatience
It is the tendency to want to have what has been bought as soon as possible. This applies fundamentally to eCommerce because in physical stores we have everything we buy on the spot.
That period of time between when the purchase occurs until the customer actually receives the product is uncomfortable. It generates some anguish or concern.
To mitigate this feeling of restlessness in the user, it is important to meet delivery deadlines.
In addition, we must explore any way that reduces the delivery time (we deliver it within the day, in two hours, etc.)
Amazon makes very good use of "impatience"; Prime users often receive their purchases on the same day.
31. Context
This bias says that perception depends on context, time and place. Context can evoke emotions and desires. The context can generate emotions and desires.
Companies like Just Eat play with this effect to their advantage and facilitate the creation of that context.
They have a product that is obviously not for daily consumption. It is a target that buys on special occasions (parties, friends' meetings, etc.)
As a strategy, the brand takes advantage of large events (parties, birthdays, etc.) and sends notifications to your email with reminders wishing you the best and sending you a discount for the night of the event.
32. Need for Simplification
The brain tries to simplify all processes and to work the minimum necessary to save energy.
For example, persuade your target about how easy it is to obtain your product or service, make it easy for them ... etc.
![FKPXLS] VOL.50 / In the long run, almost anything is possible - by Tina He - Fakepixels](https://cdn.substack.com/image/fetch/f_auto,q_auto:good,fl_progressive:steep/https%3A%2F%2Fbucketeer-e05bbc84-baa3-437e-9518-adb32be77984.s3.amazonaws.com%2Fpublic%2Fimages%2Fcff25cca-cccf-4bd7-bbb8-ccd6ecc0d661_325x284.gif)
33. Humour Effect
The messages that include humour can be more remembered and can impact more since they attract much more attention.
Laughing produces endorphins, activates the part of the brain that recognizes pleasure.
For that reason, it is always a good idea to include humour in our texts or images.
Analyze the content of your website from Neuromarketing
The brain processes images at a speed of 0.013 seconds.
It takes only 0.03 seconds to process the meaning of words and only 0.05 seconds to process the first impression that a website produces.
All of this requires us to persuade and convince quickly, effectively, and bluntly.
Further Reading :
